EPJ D Highlight - Reading between the lines of highly turbulent plasmas
- Details
- Published on 29 March 2017
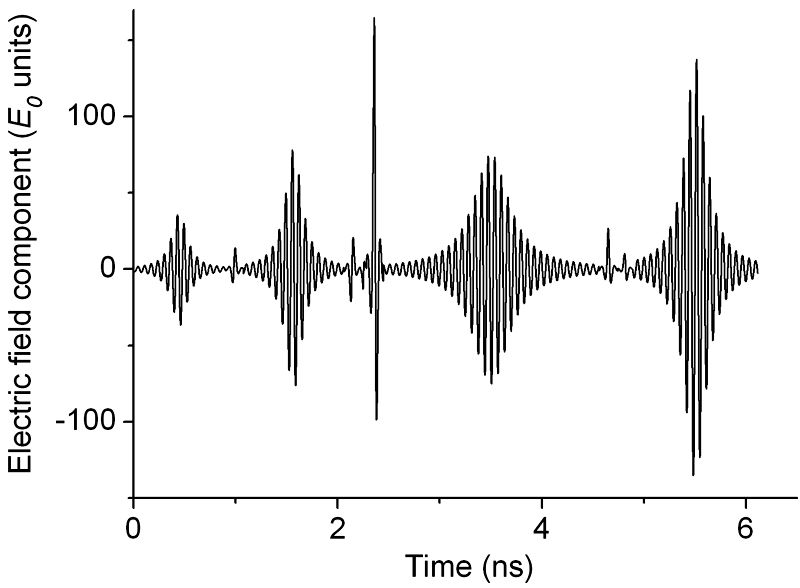
Study shows how to identify highly turbulent plasma signatures in the broadening of the shapes of lines emitted by ions and atoms within
Plasma, the ionised state of matter found in stars, is still not fully understood, largely due to its instability. Astrophysicists have long-since sought to develop models that can account for the turbulent motions inside plasma, based on observing line shapes emitted by atoms and ions in the plasma. Turbulences are typically detected through the observation of broadened lines due to the Doppler effect, similar to the principle behind radar. In a new study published in EPJ D, Roland Stamm from the CNRS and Aix-Marseille University, France, and colleagues develop an iterative simulation model that accurately predicts, for the first time, the changes to the line shape in the presence of strong plasma turbulence. Ultimately, the authors aim to provide a system for assessing plasma turbulence that is valid for both a stellar atmosphere and the ITER tokamak designed to generate fusion energy. Line shapes are extensively employed as a powerful diagnostic tool for detecting turbulences in stable gases and plasmas. For many years now, astrophysicists have developed and employed models that gauge the effect of turbulent motions in the broadening of line shapes due to the Doppler effect. Such models are now also being employed to understand the role of turbulences in plasmas created to harvest energy from fusion.
EPJ D Highlight - Ionisation mechanisms of captive atoms struck by light matter
- Details
- Published on 01 March 2017
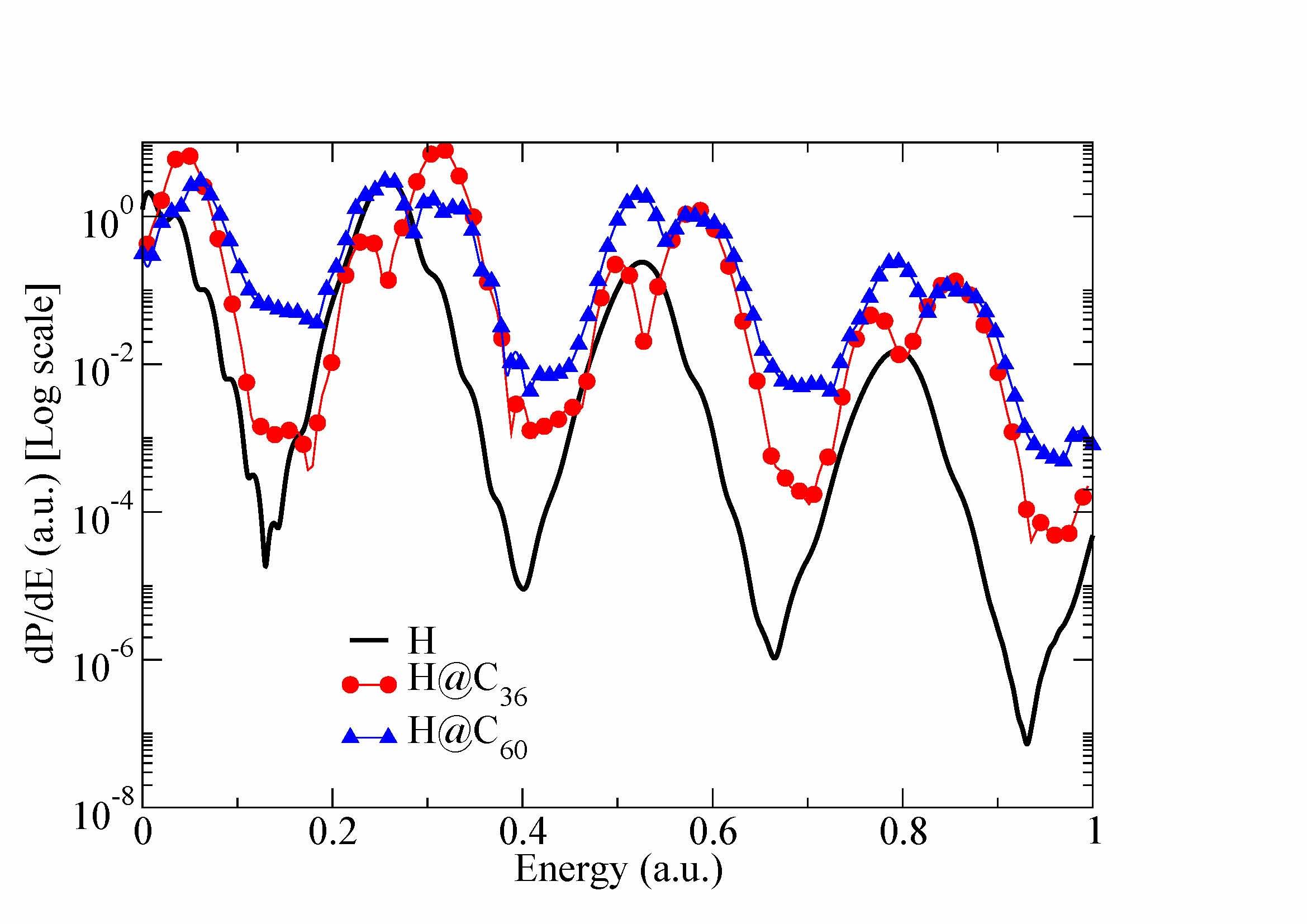
Physicists elucidate the effects of light rays falling onto hydrogen atoms trapped in a carbon atom cage
Light interacting with hydrogen atoms enclosed in hollow cages composed of carbon atoms - referred to as fullerene material - produces ionisation. This phenomenon, which has been the subject of intense theoretical scrutiny, is particularly interesting because the light rays can have dramatic effects in inducing small external energy potentials. Specifically, they alter the structural and dynamic properties of the atoms confined within the fullerene molecule. Ana Frapiccini from the CONICET research centre at the Universidad Nacional del Sur, in Bahía Blanca, Argentina, and colleagues have just published a study in EPJ D explaining the theory behind the ionisation. Applications of this process include drug delivery, quantum computation, photovoltaics and hydrogen storage.
EPJ D Highlight - Novel plasma jet offshoot phenomenon explains blue atmospheric jets
- Details
- Published on 08 February 2017
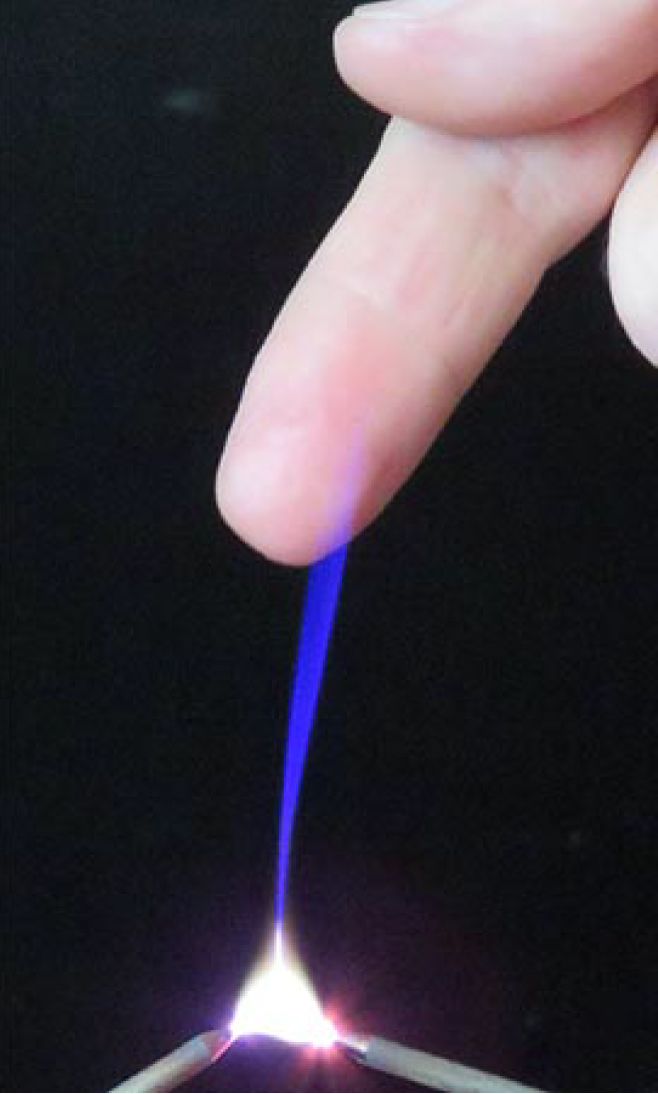

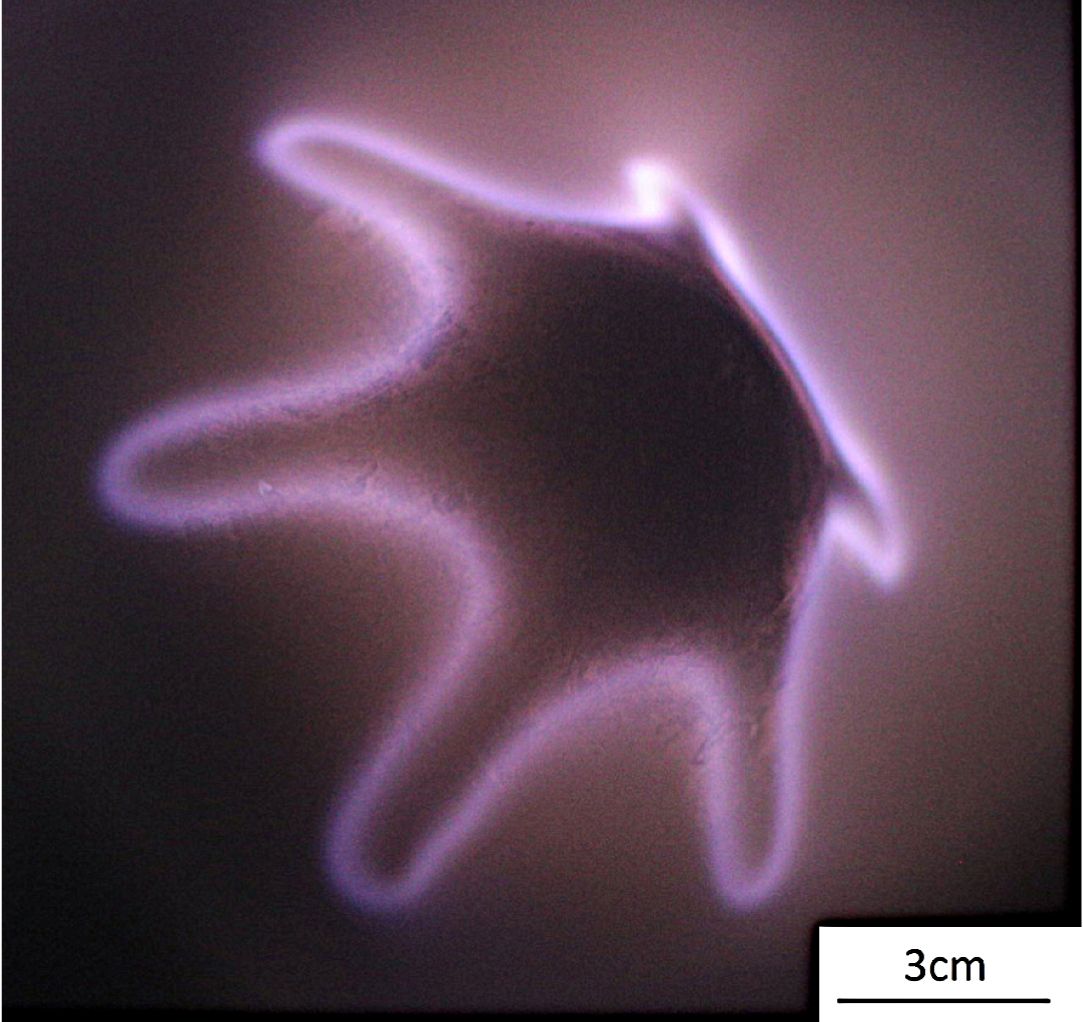
Russian physicists identify mysterious right-angle side-jet occurring off the plasma arc in air at ambient pressure conditions
Ionised matter, like plasma, still holds secrets. Physicists working with plasma jets, made of a stream of ionised matter, have just discovered a new phenomenon. Indeed, Eduard Sosnin from the Institute of High Current Electronics, Russian Academy of Sciences in Tomsk, Russia, and colleagues found a new type of discharge phenomenon in an atmospheric pressure plasma. It has been dubbed apokamp—from the Greek words for ‘off’ and ‘bend’, because it appears at a perpendicular angle to where plasma jets bend. Their findings have been recently published in EPJ D and are particularly relevant for the development of novel applications in medicine, health care and materials processing because they involve air at normal atmospheric pressure, which would make it cheaper than applications in inert gases or nitrogen.
EPJ D Colloquium: Non-equilibrium in low-temperature plasmas
- Details
- Published on 28 November 2016
The wide range of applications that have been found for cold plasmas stems from the fact that they are physical systems out of thermodynamic equilibrium. This property enhances their reactivity at low gas temperature, and allows macroscopic effects to be obtained with only moderate energy consumption.
In this EPJ D review, the basic concepts of ionised gases in a non-equilibrium state are treated by showing how and why the non-equilibrium functions of the degrees of freedom are formed in a variety of natural and man-made plasmas, with particular emphasis on the progress that has been made in the last decade. A modern perspective of the molecular basis of non-equilibrium and of a state-to-state kinetic approach is adopted. Computational and diagnostic techniques that have been used to investigate the non-equilibrium conditions are also surveyed.
EPJ D Highlight - Better than milk on breakfast cereals: new precision coating method for industrial granular material
- Details
- Published on 23 November 2016
Deposition of a thin film catalyst of a predicted thickness on the surface of novel hydrogen storage microbeads helps release hydrogen
As anyone who eats their cereal with milk in the morning knows: coating large volumes of granular material homogeneously is no mean feat. In a recent paper published in EPJ D, an Austrian team has developed a new method, based on physical vapour deposition, to upscale the quantity of coating without affecting the quality and homogeneity of the film. In this study, Andreas Eder from Vienna University of Technology and colleagues also developed a model capable of predicting the film thickness. This represents a major step forward for industrial materials, as previous approaches relied on optical measurement after the coating had been deposited. Because this coating system is capable of implementing a plasma close to the granular substrate, it opens the door to new surface treatment and modification possibilities.
EPJ D Colloquium: Evaluating experimental molecular physics studies of radiation damage in DNA
- Details
- Published on 14 November 2016
Molecular physics has made significant new contributions to our understanding of radiation damage at the molecular level, and led to improved cancer therapy through both experimental and theoretical advances, in particular the development of new damage measurement and analysis techniques.
In this EPJ D Colloquium paper, Małgorzata A. Śmiałek summarizes and highlights the most prominent findings in atomic and molecular physics, that have contributed towards a better understanding of the fundamental processes in biological systems and relevant to the next generation of radiation therapies. She also comments on the practical experimental challenges that have been met while investigating the more complex targets.
EPJ D Highlight - When quantum scale affects the way atoms emit and absorb particles of light
- Details
- Published on 20 October 2016
Exact simulation lifts the 80-year-old mystery of the degree to which atoms can be dressed with photons
In 1937, US physicist Isidor Rabi introduced a simple model to describe how atoms emit and absorb particles of light. Until now, this model had still not been completely explained. In a recent paper, physicists have for the first time used an exact numerical technique: the quantum Monte Carlo technique, which was designed to explain the photon absorption and emission phenomenon. These findings were recently published in EPJ D by Dr Flottat from the Nice –Sophia Antipolis Non Linear Institute (INLN) in France and colleagues. They confirm previous results obtained with approximate simulation methods.
EPJ D Highlight - Inside an ion-molecule collision
- Details
- Published on 19 September 2016

Physicists elucidate reactions underlying positive ion beams hitting molecular targets relevant in proton therapy
Ion-molecule reactions are ubiquitous. They are important in the emergence of primordial life as solar wind falls onto chemicals turning them into the prebiotic building blocks of life. Ion-molecule reactions are also the basic process underlying the proton-biomolecule collisions relevant in proton therapies in cancer. To better understand these mechanisms, a new study provides novel data on low-energy proton collisions with furan and its derivative molecules, which are models for the deoxyribose sugar unit found in biological processes. These findings have been published in EPJ D by Tomasz Wasowicz from Gdansk University of Technology, Poland, and colleagues, as part of the topical issue “Low-Energy Interactions related to Atmospheric and Extreme Conditions.”
Plasma Physicist Kurt H. Becker Elected to Board of Directors of National Academy of Inventors
- Details
- Published on 04 July 2016

EPJ D Highlight - Electron scavenging to mimic radiation damage
- Details
- Published on 29 June 2016
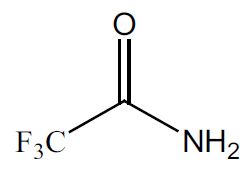
New study could help unveil negative effect of radiation on biological tissues due to better understanding of low energy electron-induced reactions
High energy radiation affects biological tissues, leading to short-term reactions. These generate, as a secondary product, electrons with low energy, referred to as LEEs, which are ultimately involved in radiation damage. In a new study, scientists study the effect of LEEs on a material called trifluoroacetamide (TFAA). This material was selected because it is suitable for electron scavenging using a process known as dissociative electron attachment (DEA). These findings were recently published in EPJ D by Janina Kopyra of Siedlce University, Poland, and colleagues in Germany, as part of a topical issue on Advances in Positron and Electron Scattering.





