EPJ D Highlight - Chemotherapy drugs react differently to radiation while in water
- Details
- Published on 30 July 2019

A new study looked at the way certain molecules found in chemotherapy drugs react to radiation while in water, which is more similar to in the body, compared to previous research that studied them in gas
Cancer treatment often involves a combination of chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Chemotherapy uses medication to stop cancer cells reproducing, but the medication affects the entire body. Radiotherapy uses radiation to kill the cancer cells, and it is targeted to the tumour site. In a recent study, published in the journal EPJ D, researchers from the Leopold-Franzens-University Innsbruck, Austria, studied selected molecules of relevance in this context. They wanted to see how these molecules were individually affected by radiation similar to that used in radiotherapy.
EPJ D Highlight - Laser solitons: theory, topology and potential applications
- Details
- Published on 23 July 2019
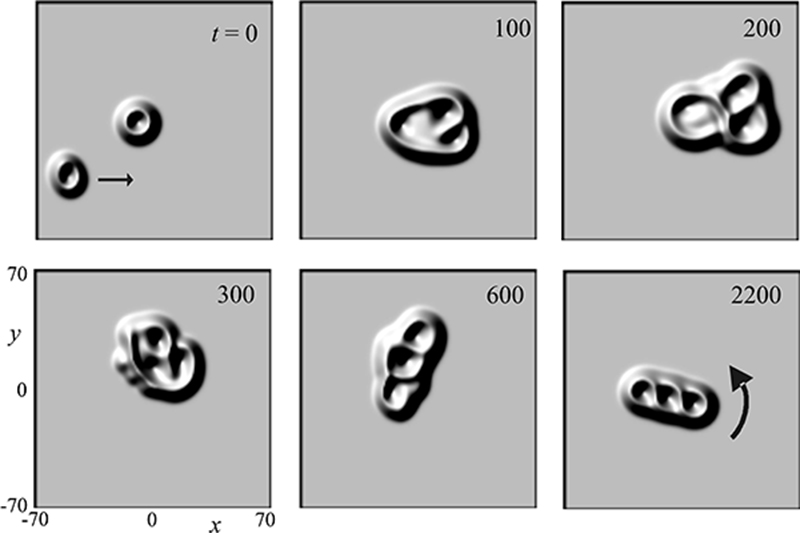

A group of Russian physicists reviews recent developments in the field of laser solitons, which they have made their own and which may have applications in digital information storage.
In almost all situations, even in a vacuum, light cannot travel endlessly without dissipating. Pulses of light known as solitons that propagate along fibres for long distances without changing their shape or losing focus have found applications in data transmission, but even these gradually dissipate unless the medium they travel through has ultra-low absorbance. Nikolay Rosanov of the National Research University of Information Technologies, Mechanics, and Optics (ITMO), St. Petersburg, Russia and his team have been working on a solution to this problem - laser solitons - since the 1980s; a colloquium paper summarising their recent work in this area has now been published in EPJ D.
EPJ D Highlight - Simulations fix the cracks in magnetic mirrors
- Details
- Published on 01 July 2019
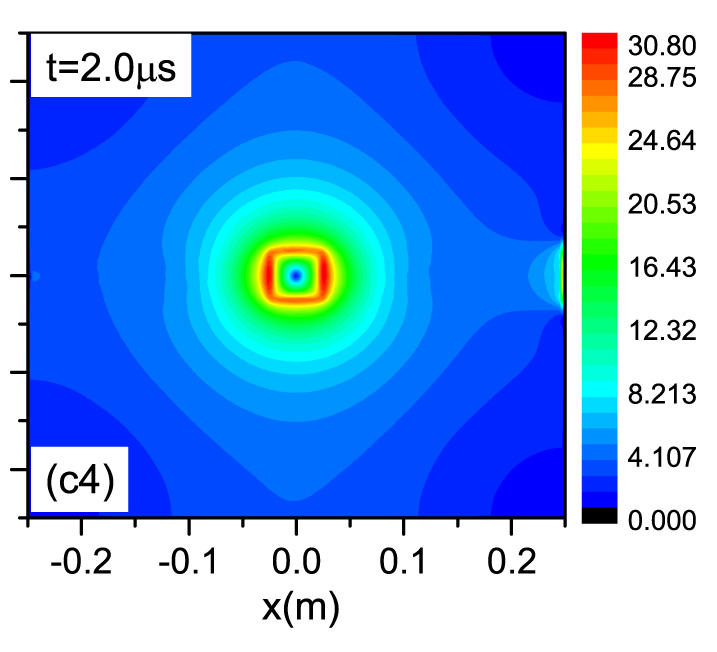
Computer simulations reveal that magnetic mirrors can be tweaked to confine plasma more effectively, by fine-tuning both the arrangements of their electromagnets, and the initial properties of the plasma itself
When ring-shaped electromagnets are set up in linear arrangements, they can produce magnetic fields resembling a tube with a cone at each end; a structure which repels charged particles entering one cone back along their path of approach. Referred to as ‘magnetic mirrors’, these devices have been known to be a relatively easy way to confine plasma since the 1950s, but they have also proven to be inherently leaky. In a study published in EPJ D, physicists led by Wen-Shan Duan at Northwest Normal University, and Lei Yang at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, both in Lanzhou, China, show that these plasma leaks can be minimised if specific conditions are met. Using computer simulations, the physicists analysed the dynamic properties of a high-energy proton plasma beam within a magnetic mirror and fine-tuned the simulation settings to maximise its confinement.
EPJD Topical review - Plasma potential probes for hot plasmas
- Details
- Published on 22 May 2019

Plasma probes are well-established diagnostic tools, being relatively simple to construct and easy to handle. The most easily accessible parameter is the floating potential, but the floating potential of a cold probe is not very significant; much more important and relevant is the plasma potential. However, in most types of plasmas, consisting mainly of electrons and only positive ions, the higher mobility of the electrons means that the floating potential is more negative than the plasma potential by a factor proportional to the electron temperature.
In a new Topical Review in EPJD co-authored by teams from Austria, Slovenia, Denmark and Italy, the authors present a review of probes whose floating potential is close or ideally equal to the plasma potential. Such probes are known as Plasma Potential Probes (PPP), and they can either be Electron Emissive Probes (EEPs) or so-called Electron Screening Probes (ESPs). These probes make it possible to measure the plasma potential directly and thus with high temporal resolution.
EPJ D Highlight - Inner electrons behave differently in aromatic hydrocarbons
- Details
- Published on 09 April 2019
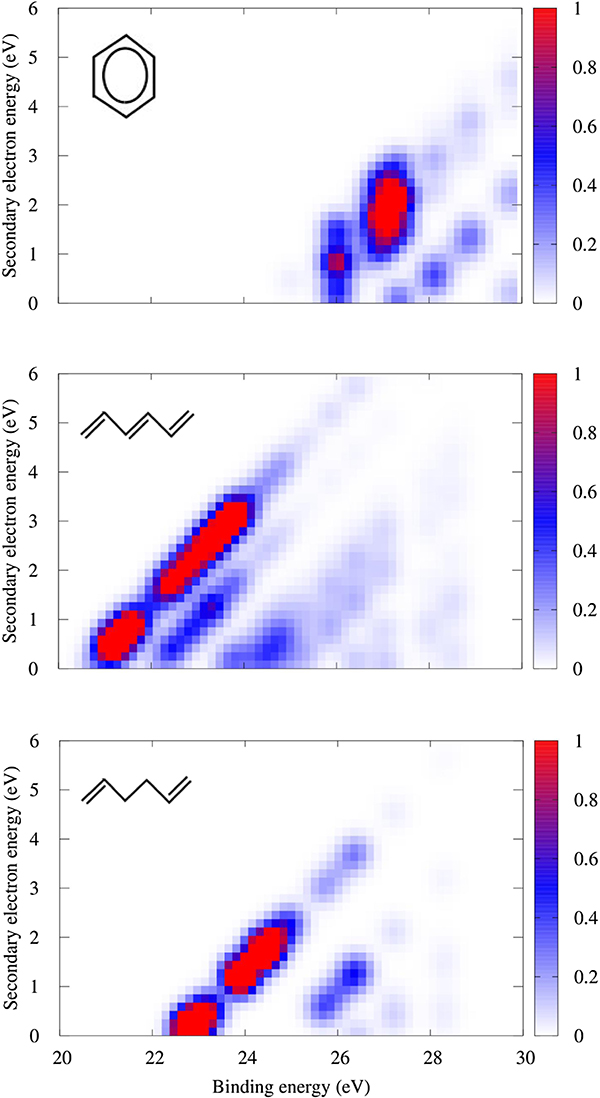
A new study explores how the characteristics of aromaticity affect the process of Auger decay
When an electron from one of the lower energy levels in an atom is knocked out of the atom, it creates a space which can be filled by one of the higher-energy electrons, also releasing excess energy. This energy is released in an electron called an Auger electron - and produces an effect known as Auger decay. Now, Guoke Zhao from Tsinghua University in Beijing, China and colleagues at Sorbonne University in Paris, France have studied the Auger effect in four hydrocarbon molecules: benzene, cyclohexane, hexatriene and hexadiene. These molecules were chosen because they exhibit different characteristics of aromaticity. The authors found that molecules containing pi bonds have a lower threshold for Auger decay.
EPJ D Highlight - Optimising proton beam therapy with mathematical models
- Details
- Published on 02 April 2019
New model improves our understanding of energy transfer in radiotherapy treatment plans by replacing 50-year-old parameters with more complex ones
Particle beam therapy is increasingly being used to treat many types of cancer. It consists in subjecting tumours to beams of high-energy charged particles such as protons. Although more targeted than conventional radiotherapy using X-rays, this approach still damages surrounding normal tissue. To design the optimum treatment plan for each patient, it is essential to know the energy of the beam and its effect on tumour and normal tissue alike. In a recent study published in EPJ D, a group of researchers led by Ramin Abolfath at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas, USA, put forward a new mathematical model outlining the effects of these beam therapies on patients' tissues, based on new, more complex, parameters. Using these new models, clinicians should be able to predict the effect of proton beams on normal and tumour tissue more precisely, allowing them to prepare more effective treatment plans.
EPJ D Highlight - Electron-gun simulations explain the mechanisms of high-energy cosmic rays
- Details
- Published on 06 February 2019
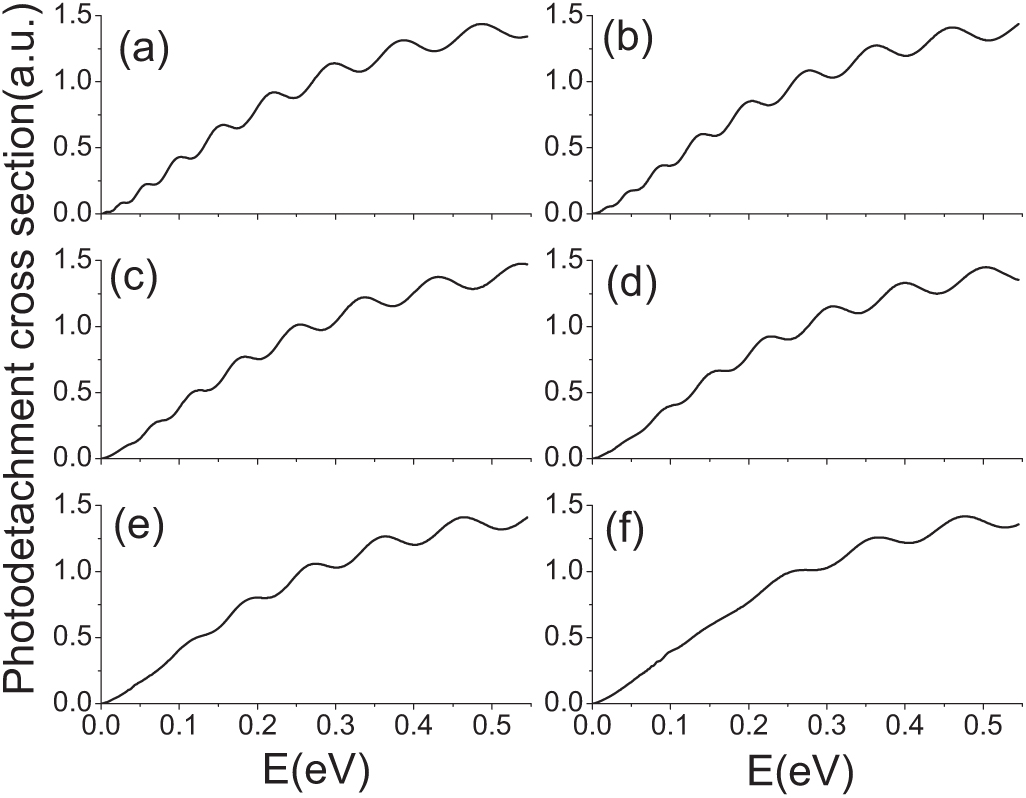
Model explains the mechanisms of scraping negative ions from moving surfaces under a strong electric field
When cosmic rays collide with planets or debris, they lose energy. Scientists use the collision of electrons with a moving surface to simulate this process. A new study published in EPJ D provides a rudimentary model for simulating cosmic rays’ collisions with planets by looking at the model of electrons detached from a negative ion by photons. In this work, Chinese physicists have for the first time demonstrated that they can control the dynamics of negative ion detachment via photons, or photodetachment, on a moving surface.
EPJ D Highlight - Better safeguards for sensitive information
- Details
- Published on 23 January 2019
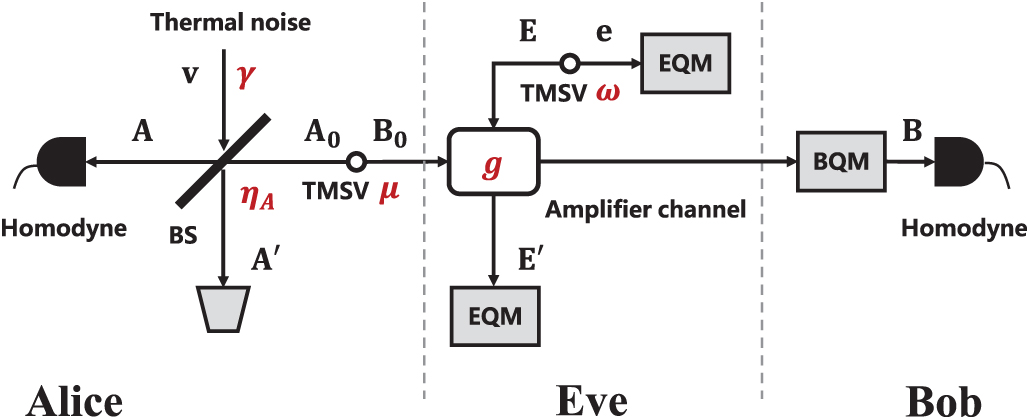
Study improves the lower boundary and secret key capacity of an encryption channel
The secure encryption of information units based on a method called quantum key distribution (QKD) involves distributing secret keys between two parties - namely, Alice, the sender, and Bob, the receiver - by using quantum systems as information carriers. However, the most advanced quantum technology, QKD, is currently limited by the channel's capacity to send or share secret bits. In a recent study published in EPJ D, Gan Wang, who is affiliated with both Peking University, Bejing, China, and the University of York, UK, and colleagues show how to better approach the secret key capacity by improving the channel's lower boundary.
EPJ D Highlight - Quantifying how much quantum information can be eavesdropped
- Details
- Published on 22 January 2019

New study yields more precise characterisation of monogamous and polygamous entanglement of quantum information units
Encrypted communication is achieved by sending quantum information in basic units called quantum bits, or qubits. The most basic type of quantum information processing is quantum entanglement. However, this process remains poorly understood. Better controlling quantum entanglement could help to improve quantum teleportation, the development of quantum computers, and quantum cryptography. Now, a team of Chinese physicists have focused on finding ways to enhance the reliability of quantum secret sharing. In a new study published in EPJ D, Zhaonan Zhang from Shaanxi Normal University, Xi'an, China, and colleagues provide a much finer characterisation of the distributions of entanglement in multi-qubit systems than previously available. In the context of quantum cryptography, these findings can be used to estimate the quantity of information an eavesdropper can capture regarding the secret encryption key.
EPJ D Highlight - Fullerene compounds made simulation-ready
- Details
- Published on 14 November 2018

New model helps understand compound nanomolecules made of football-shaped fullerenes
What in the smart nanomaterials world is widely available, highly symmetrical and inexpensive? Hollow carbon structures, shaped like a football, called fullerenes. Their applications range from artificial photosynthesis and nonlinear optics to the production of photoactive films and nanostructures. To make them even more flexible, fullerenes can be combined with added nanostructures. In a new study published in EPJ D, Kirill B. Agapev from ITMO University, St. Petersburg, Russia, and colleagues have developed a method that can be used for future simulations of fullerene complexes and thus help understand their characteristics.




